What Is The Cloud

Cloud computing has become an integral part of most people’s lives today and yet it remains a nebulous topic to many. We often back up our pictures and files on “the cloud” and that is the extent of the knowledge most people have about it. Although cloud infrastructure is often referred to as “the cloud”, it is not a singular entity. The infrastructure includes all of the things that make up the framework of the cloud including the servers, network, software, and storage.
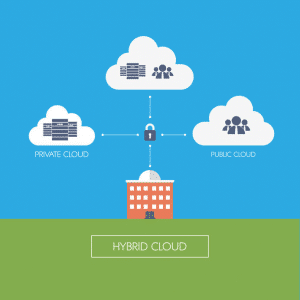
Cloud infrastructure can be deployed in multiple ways. This is important to determine how the cloud platform will be hosted, who has access to it, and who controls it. Naturally, each deployment model has varying costs, advantages, and disadvantages. The 4 cloud deployment models are public cloud, private clouds, hybrid clouds, and community clouds.
The Cloud Deployment Models
- Private Clouds – If a company uses a private cloud, then they are the only ones who access it. The cloud could actually be within the company or it could be at an off-site location. The private cloud must be managed and maintained by the organization itself which can be expensive. On the other hand, private clouds offer more security and a higher level of control for the organization.
- Public Clouds – With public clouds, a cloud provider rents out cloud resources to customers through an open cloud. This is generally how the cloud offerings of the big tech companies like Microsoft and Google are structured. The cloud infrastructure and resources are typically shared between all customers. This model reduces costs as the customer no longer needs to worry about problems like server maintenance and handling back-ups. The customer loses control however as significant changes can’t be made to the server’s hardware or software because they do not actually own them. This could also lead to potential security vulnerabilities if the provider is not properly patching their servers.
- Hybrid Clouds – In this deployment an organization utilizes a combination of public and private clouds. Data can be seamlessly moved between the two cloud infrastructures as needed. This helps securely move large amounts of data into a collaborative public environment as needed. The primary advantage here is scalability. An organization can easily use a public cloud to increase resources to meet higher demands and traffic.
- Community Clouds – Community clouds are also a type of hybrid between public and private clouds. The cloud infrastructure is privately managed but is accessed only by a specific group of organizations. This type is not commonly used outside of specific professional communities like government agencies, healthcare organizations, or police departments. The advantage of this deployment is that it makes it easy for a group of organizations to collaborate on projects or research.
If it wasn’t obvious by now, most individuals are enjoying the benefits of public clouds when they refer to “the cloud”. There is still a lot more to learn about cloud computing and next time we will discuss the different types of cloud computing services.